views
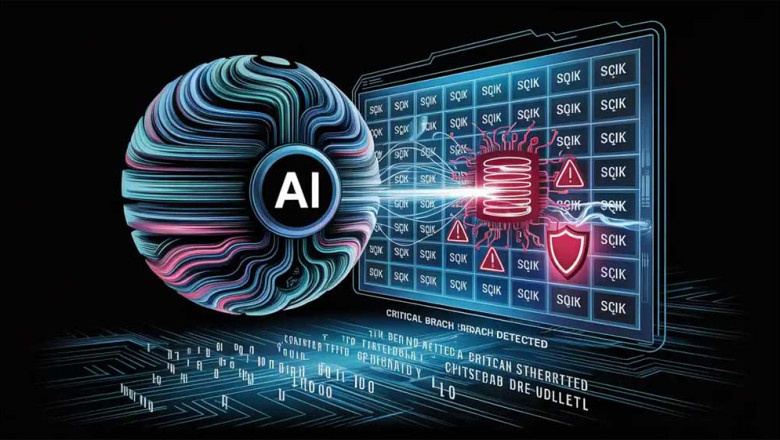
Google's AI agent Big Sleep recently discovered a critical security flaw in SQLite, an open-source database engine widely used across software applications123. This vulnerability, officially tracked as CVE-2025-6965, is a stack buffer underflow involving improper handling of negative indices, which could allow attackers to perform arbitrary read or write operations outside the intended memory bounds, potentially leading to crashes or arbitrary code execution19.
What makes this discovery significant is that the flaw was previously unknown and known only to threat actors — it was on the verge of being exploited in the wild25. Big Sleep, developed collaboratively by Google DeepMind and Google Project Zero, combined large language model (LLM) technology with threat intelligence to proactively detect the vulnerability before it caused harm, enabling a swift patch25.
Big Sleep's approach goes beyond traditional methods like fuzzing. It uses advanced AI techniques such as variant analysis, root-cause analysis, and code pattern recognition to autonomously scan large codebases for subtle and complex vulnerabilities that conventional tools can miss49. It analyzes changes like commit diffs and simulates real-world conditions to identify exploitable bugs9.
Google described this as a milestone in cybersecurity: the first time an AI agent has not only found a previously unknown critical vulnerability but has also directly intervened to thwart an imminent cyberattack2. CEO Sundar Pichai noted this achievement as a first step toward AI-driven defense becoming a standard, with Big Sleep helping to scale human security expertise and accelerate vulnerability research25.
Beyond this discovery, Google plans to continue expanding AI-powered security tools for both its own products and widely used open-source projects, aiming to shift cybersecurity from reactive patching to proactive threat prediction and prevention5.
In summary:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| AI Agent | Big Sleep (from Google DeepMind and Project Zero) |
| Vulnerability discovered | Critical stack buffer underflow in SQLite (CVE-2025-6965) |
| Vulnerability type | Buffer underflow due to negative index handling, leading to possible arbitrary memory access |
| Impact | Vulnerability at risk of exploitation in the wild; could lead to crashes or code execution |
| Significance | First AI agent to find and directly block an imminent exploit |
| Methodology | Large language models with variant analysis, root-cause analysis, code simulation |
| Outcome | Vulnerability patched before official release, preventing impact |
This breakthrough demonstrates AI’s growing role as a powerful ally in cybersecurity, enhancing defenders' ability to find and mitigate threats more efficiently and safely125.
- https://thehackernews.com/2024/11/googles-ai-tool-big-sleep-finds-zero.html
- https://theoutpost.ai/news-story/google-s-ai-agent-big-sleep-thwarts-cyberattack-before-it-begins-17795/
- https://googleprojectzero.blogspot.com/2024/10/from-naptime-to-big-sleep.html
- https://winbuzzer.com/2024/11/02/googles-big-sleep-ai-agent-uncovers-exploitable-bug-in-sqlite-xcxwbn/
- https://blog.google/technology/safety-security/cybersecurity-updates-summer-2025/
- https://www.techmeme.com/250716/p6
- https://www.darkreading.com/application-security/google-big-sleep-ai-agent-sqlite-software-bug
- https://www.techmeme.com/250716/p14
- https://siliconangle.com/2024/11/05/googles-big-sleep-ai-model-sets-world-first-discovery-sqlite-security-flaw/
- https://techurls.com
- https://www.datanami.com/2024/11/07/googles-new-ai-tool-uncovers-critical-zero-day-vulnerability-in-sqlite/
- https://www.itnews.com.au/news/googles-big-sleep-security-ai-agent-foils-bug-exploitation-618787


















Comments
0 comment