
views
World Energy Crisis Would Be Worse Without China’s Rainy Season
As bad as the world’s energy crisis has been this year, it would been much worse without a wetter-than-usual start to China’s rainy season.
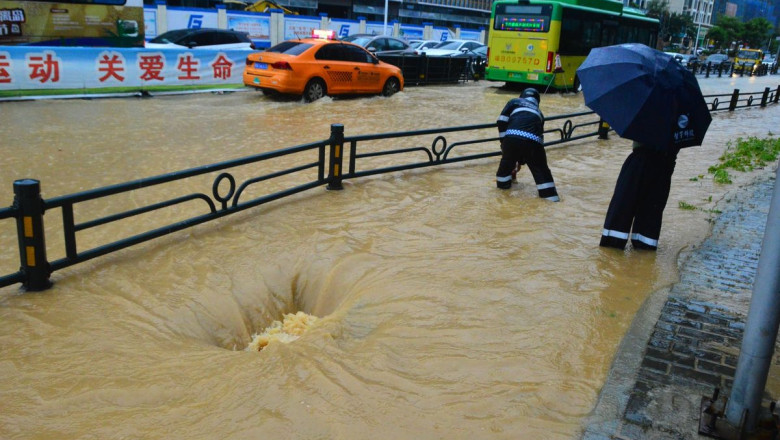
While heavy downpours in southern China have been a public safety crisis, closing schools and causing fatalities, they’ve also led to reduced air-conditioning demand and surging hydropower generation. Both have lessened the need for fossil fuels, allowing the world’s biggest coal and gas importer to cut purchases and leave more supply for other energy-starved nations.
Hydro is still China’s biggest carbon-free energy resource, accounting for about as much power as solar, wind and nuclear combined, although growth has flattened as topography limits expansion.
Hydropower generation through the end of May rose 18% from last year as rains filled reservoirs and two massive projects along tributaries of the Yangtze River ramped up output. The additional power would have consumed about 27 million tons of coal if it had come from thermal plants, based on data from the US Energy Information Administration.
“Regions importing hydropower from southwest China are certainly able to alleviate some pressure of high thermal fuel costs,” said David Fishman, a Shanghai-based analyst with The Lantau Group.
At the same time, rains helped keep temperatures cool in southern China, where intense heat in May and June last year contributed to a coal shortage that forced local governments to cut off power to factories. This May, the economic powerhouse of Guangdong province saw power consumption drop 15% from the previous year, saving about 4.6 million tons of coal.
Alongside stringent virus restrictions in Shanghai and northern China, the rains have helped suppress fossil fuel usage so that thermal power generation recorded a 3.5% annual drop through the end of May, the worst annual performance for the first five months since 2016. That’s cut imports of coal by 14% and liquefied natural gas by 20%, just as international prices have soared after Russia invaded Ukraine.
Alongside stringent virus restrictions in Shanghai and northern China, the rains have helped suppress fossil fuel usage so that thermal power generation recorded a 3.5% annual drop through the end of May, the worst annual performance for the first five months since 2016. That’s cut imports of coal by 14% and liquefied natural gas by 20%, just as international prices have soared after Russia invaded Ukraine.
And there’s no telling where global prices would be without that reduction. China has demonstrated it’s willing to stump up whatever it takes for energy security, and officials are taking the same line this year with promises that factories won’t face the same curtailments that struck last summer and fall.
Events Today
(All times Beijing unless shown otherwise.)
Markets Latest |
|
| Copper -0.4% in Shanghai | Crude oil +2.4% in Shanghai |
| Aluminum +1.4% in Shanghai | Nickel +1.4% in Shanghai |
| Iron ore -2.8% in Dalian | Steel rebar -1.8% in Shanghai |
| Thermal coal -1.9% in Zhengzhou | Coking coal -2.9% in Dalian |
| Live hogs +2.5% in Dalian | Corn +0.7% in Dalian |
On The Wire
China’s top economic planning agency will meet with major pig farming companies on Monday to study measures to keep the pork market stable, Cailian reported. Shares of pig breeders rose.
The Week Ahead
Tuesday, July 5
Wednesday, July 6
Thursday, July 7
Friday, July 8
Saturday, July 9
Sunday, July 10


















Comments
0 comment